알고리즘 풀이(JAVA) - 백준 알고리즘_1992(쿼드 트리)
By on October 20, 2019
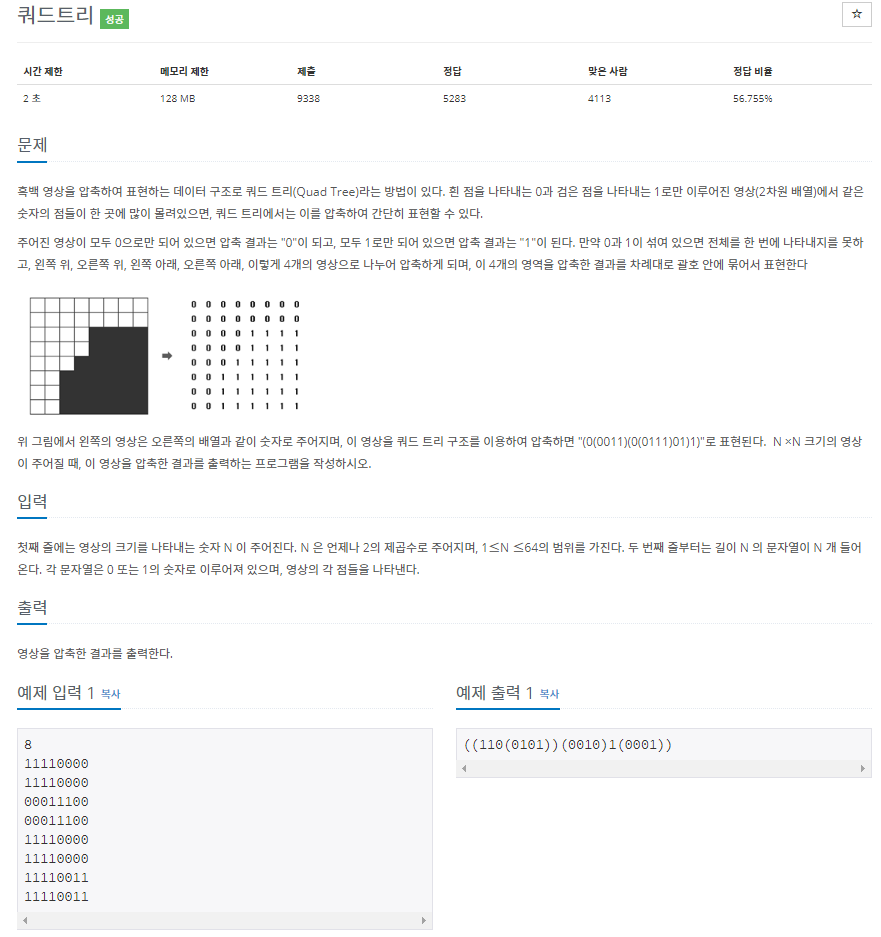
문제
문제 링크 : https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1992
풀이
이 문제는 앞선 색종이 자르기https://parkhyeokjin.github.io/algorithm/2019/08/22/baekjoon-2630.html 를 풀어 보았다면 쿼드 트리를 이용해서 쉽게 해결 할 수 있다.
-
쿼드 트리는 4개의 자식 노드를 가지는 트리 구조이다.
- 영상 입력 처리 readData(reader, N)
- 재귀 함수(cut()) 를 이용 하여 4부분으로 반복적으로 자른다.
- 잘려진 영역의 문자열이 동일할 경우 압축 한다.
- 잘려진 영역의 문자열이 동일 하지 않을 경우 다시 4부분으로 자른다.
소스
- 쿼드 트리(1992)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Baekjoon_1992 {
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
public static void main(String[] args){
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
try{
int N = Integer.parseInt(reader.readLine());
int[][] movie = readData(reader, N);
cut(movie);
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static int[][] readData(BufferedReader reader, int N) throws IOException {
int[][] movie = new int[N][N];
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String[] readStr = reader.readLine().split("");
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
movie[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(readStr[j]);
}
}
return movie;
}
/*
* 재귀 함수.
* 주어진 문자열을 하나의 문자로 압축 될때 까지 반복해서 4부분으로 자른다.
*/
private static void cut(int[][] num){
if(compression(num)) {
return;
}else {
sb.append("(");
int half = num.length / 2;
cut(cutMovie(num, 0, half, 0, half));
cut(cutMovie(num, 0, half, half, num.length));
cut(cutMovie(num, half, num.length, 0, half));
cut(cutMovie(num, half, num.length, half, num.length));
sb.append(")");
}
}
private static int[][] cutMovie(int[][] num, int xS, int xE, int yS, int yE) {
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int[][] tmp = new int[num.length/2][num.length/2];
for(int x = xS; x < xE; x++) {
for (int y = yS; y < yE; y++) {
tmp[i][j++] = num[x][y];
}
i++;
j = 0;
}
return tmp;
}
/*
* 문자열 비교(압축)
* 주어진 문자열을 비교 하여 하나의 문자열으로 압축 될 경우 StringBuilder 에 해당 문자를 입력하고
* 하나의 문자열로 압축이 되지 않을 경우 return false 를 전달 하여 재귀 함수에서 다시 처리 되도록 한다.
*/
private static boolean compression(int[][] num) {
int[] numCnt = new int[2];
for(int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < num.length; j++) {
numCnt[num[i][j]] += 1;
}
}
if(numCnt[0] > 0 && numCnt[1] > 0 ) {
return false;
}else {
if(numCnt[0] > 0 && numCnt[1] == 0) {
sb.append(0);
}else {
sb.append(1);
}
return true;
}
}
}