그래프 알고리즘 기초 - 다익스트라(Dijkstra)
By on November 22, 2023
그래프 알고리즘 기초 - 다익스트라(Dijkstra)
다익스트라(Dijkstra)
- 다익스트라 알고리즘은 시작노드에서 모든 노드로의 최단거리를 찾는 알고리즘입니다.
- 참고사항
- 시간복잡도(노드수 : v, 에지 수 : E) : O(Elogv)
- 음수 가중치가 있는경우 사용 할 수 없음. 음수 가중치가 있는 경우 벨만포드 알고리즘(Bellman-Ford) 을 사용.
- 알고리즘 활용 영역
- 백준 1753 - 최단경로 https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1753
다익스트라 구현 코드(백준-최단경로)
public class BJ_1753 {
/**
* 방향그래프가 주어지면 주어진 시작점에서 다른 모든 정점으로의 최단 경로를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오. 단, 모든 간선의 가중치는 10 이하의 자연수이다.
* 첫째 줄에 정점의 개수 V와 간선의 개수 E가 주어진다. (1 ≤ V ≤ 20,000, 1 ≤ E ≤ 300,000) 모든 정점에는 1부터 V까지 번호가 매겨져 있다고 가정한다.
* 둘째 줄에는 시작 정점의 번호 K(1 ≤ K ≤ V)가 주어진다. 셋째 줄부터 E개의 줄에 걸쳐 각 간선을 나타내는 세 개의 정수 (u, v, w)가 순서대로 주어진다.
* 이는 u에서 v로 가는 가중치 w인 간선이 존재한다는 뜻이다. u와 v는 서로 다르며 w는 10 이하의 자연수이다. 서로 다른 두 정점 사이에 여러 개의 간선이 존재할 수도 있음에 유의한다.
*
*
* 입력값
*
5 6
1
5 1 1
1 2 2
1 3 3
2 3 4
2 4 5
3 4 6
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] VE = br.readLine().split(" ");
int v = Integer.parseInt(VE[0]);
int e = Integer.parseInt(VE[1]);
int k = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int[] answer = new int[v + 1]; //각 노드에서 최단거리를 입력할 결과 배열 (시작노드는 0으로, 나머지는 무한대(∞)로 입력한다.)
Arrays.fill(answer, Integer.MAX_VALUE); //가장 큰값으로 초기화
boolean[] visited = new boolean[v + 1]; //방문 정보관리
List<Node>[] nodes = new ArrayList[v+1]; //2차원 배열을 생성 하여 그래프 정보를 입력한다.
for(int i = 0; i <= v; i++){
nodes[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for(int i = 0; i < e; i ++){
String[] SEV = br.readLine().split(" ");
int sn = Integer.parseInt(SEV[0]); //시작 노드
int en = Integer.parseInt(SEV[1]); //종료(다음) 노드
int vn = Integer.parseInt(SEV[2]); //가중치
nodes[sn].add(new Node(en, vn)); //2차원 배열에 입력. list의 Index(sn) 가 노드 번호가 된다.
}
Dijkstra(visited, nodes, answer, k);
//출력 부분-------------------
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = 1; i < answer.length; i++){
if(answer[i] == Integer.MAX_VALUE){
sb.append("INF").append("\n"); //더이상 갈수 있는 노드가 없다면 INF 로 출력 (무한대(∞) 로 남아있다는 것은 더이상 갈 수 있는 노드가 없다는 것을 뜻함.)
continue;
}
sb.append(answer[i]).append("\n");
}
System.out.println(sb); // 출력 : 0, 2, 3, 7, INF
//출력 부분-------------------
}
private static void Dijkstra(boolean[] visited, List<Node>[] nodes, int[] answer, int k) {
PriorityQueue<Node> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
queue.add(new Node(k, 0));
answer[k] = 0; //시작 노드는 0으로 초기화.
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Node curNode = queue.poll();
if(visited[curNode.end]){
continue; //방문한 노드이면 패스.
}
visited[curNode.end] = true; //방문 체크
for(Node nextNode : nodes[curNode.end]){
if(answer[nextNode.getEnd()] > answer[curNode.getEnd()] + nextNode.weight){
answer[nextNode.getEnd()] = answer[curNode.getEnd()] + nextNode.weight; //가중치 업데이트
queue.add(new Node(nextNode.getEnd(), answer[nextNode.getEnd()]));
}
}
}
}
public static class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
private int end;
private int weight;
public Node(int end, int weight) {
this.end = end;
this.weight = weight;
}
public int getEnd() {
return end;
}
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return weight - o.weight;
}
}
}
풀이
주어진 그래프는 아래와 같습니다.
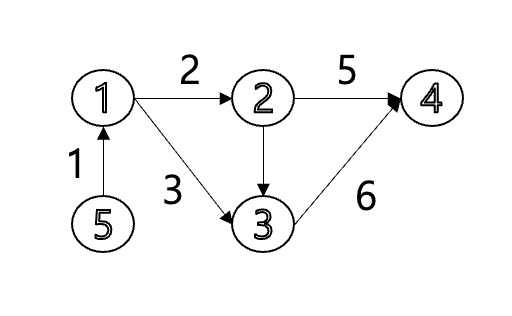
- 결과
노드번호 1 2 3 4 5
최단거리 : 0, 2, 3, 7, INF
결과에서 보듯이 시작노드(K = 1) 에서 갈 수 있는 최단경로 가중치가 구해진걸 확인 할 수 있습니다.
- 1 -> 2 으로 가는 최단경로의 가중치는 2
- 1 -> 3 으로 가는 최단경로의 가중치는 3
- 1 -> 4 으로 가는 최단경로의 가중치는 7 (1 -> 2-> 4 의 경로로 이동)
- 1 -> 5 는 갈 수 없기 때문에 INF