Request-Reply Pattern Using Kafka (in Enterprise Integration Patterns)
By on June 13, 2024
Request-Reply Pattern 이란?
Request-Reply Pattern 은 엔터프라이즈 통합 패턴 중 하나로 비동기적인 요청-응답 처리를 가능 하게 하는 방식 입니다. 일반적인 Request-Response 패턴은 요청을 보내면 즉시 응답을 받지만 Request-Reply 패턴은 응답을 특정 수신 채널을 통해 비동기적으로 처리 할 수 있어 시스템간 결합도를 줄이고 유연성을 높일 수 있는 패턴 입니다.
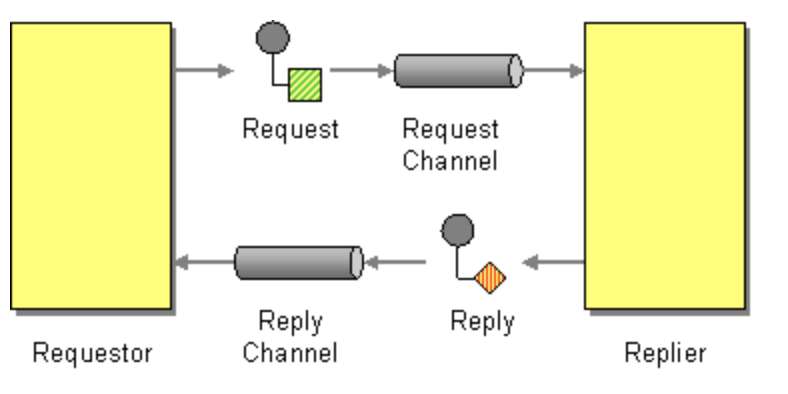
- 참조 링크 : https://www.enterpriseintegrationpatterns.com/patterns/messaging/RequestReply.html
Kafka 를 이용한 Request-Reply 패턴 구현
제가 속해 있는 선불서비스 팀은 이벤트 기반 아키텍처(Event Driven Architecture) 를 적극 활용 하고 있습니다. 다양한 이벤트를 MSK(Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka) 를 통해 발행하여 가용성과 재활용성을 극대화하는데 노력 하고 있습니다. 일반적인 RestAPI 구조에서 이벤트를 활용 하여 어떻게 비동기 이벤트를 활용 할까 고민 하는 중에 Spring 에서 제공 하는 ReplyingKafkaTemplate 를 발견하여 해당 기능을 POC(Proof of Concept) 하였고 이를 활용하여 다양한 기능에 활용 할 수 있을 것으로 검증하여 이에 대한 내용을 기록 합니다.
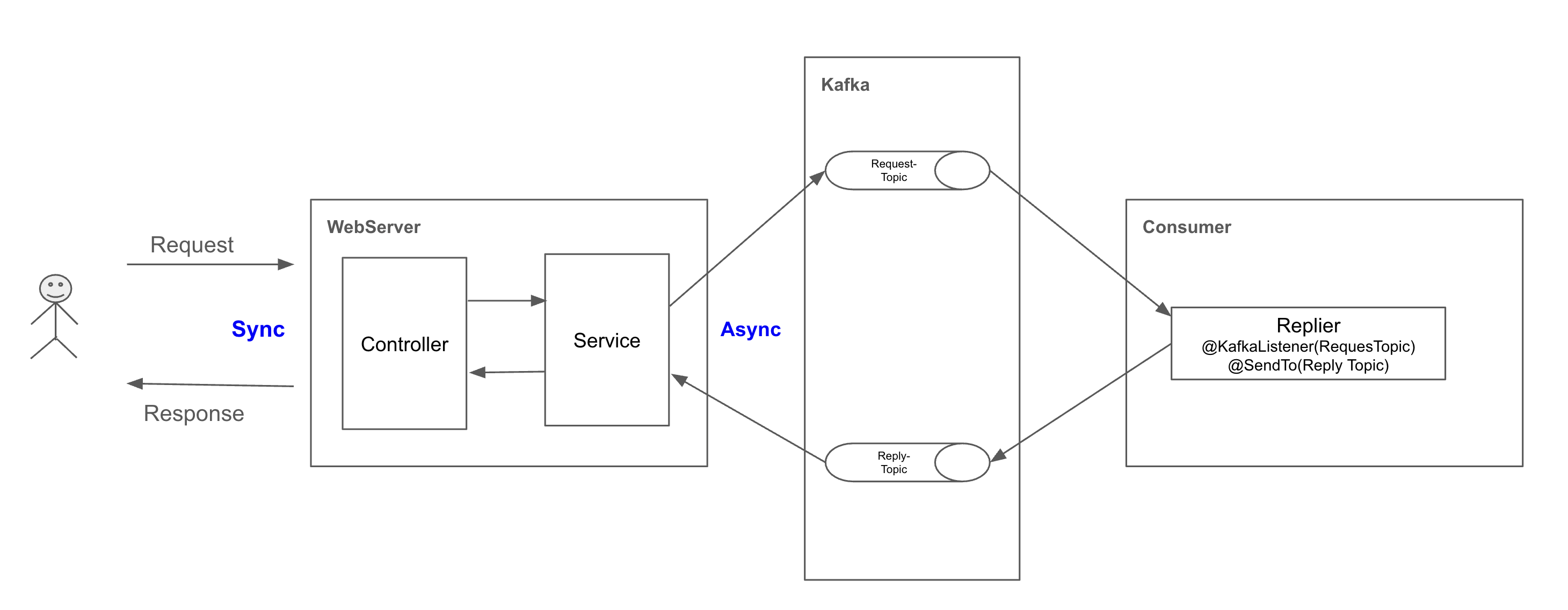
ReplyingKafkaTemplate
흔히 사용 하는 KafkaTemplate 은 Send() 메서드를 제공하지만 ReplyingKafkaTemplate 는 sendAndReceive() 메서드를 제공합니다.
class KafkaTemplate{
public CompletableFuture<SendResult<K, V>> send(String topic, @Nullable V data) {
ProducerRecord<K, V> producerRecord = new ProducerRecord(topic, data);
return this.observeSend(producerRecord);
}
public CompletableFuture<SendResult<K, V>> send(String topic, K key, @Nullable V data) {
ProducerRecord<K, V> producerRecord = new ProducerRecord(topic, key, data);
return this.observeSend(producerRecord);
}
}
class ReplyingKafkaTemplate{
public RequestReplyMessageFuture<K, V> sendAndReceive(Message<?> message) {
return this.sendAndReceive(message, this.defaultReplyTimeout, (ParameterizedTypeReference)null);
}
public RequestReplyMessageFuture<K, V> sendAndReceive(Message<?> message, Duration replyTimeout) {
return this.sendAndReceive(message, replyTimeout, (ParameterizedTypeReference)null);
}
public <P> RequestReplyTypedMessageFuture<K, V, P> sendAndReceive(Message<?> message, @Nullable Duration replyTimeout, @Nullable ParameterizedTypeReference<P> returnType) {
RequestReplyFuture<K, V, R> future = this.sendAndReceive(this.getMessageConverter().fromMessage(message, this.getDefaultTopic()), replyTimeout);
RequestReplyTypedMessageFuture<K, V, P> replyFuture = new RequestReplyTypedMessageFuture(future.getSendFuture());
future.whenComplete((result, ex) -> {
if (ex == null) {
try {
replyFuture.complete(this.getMessageConverter().toMessage(result, (Acknowledgment)null, (Consumer)null, returnType == null ? null : returnType.getType()));
} catch (Exception var6) {
Exception ex2 = var6;
replyFuture.completeExceptionally(ex2);
}
} else {
replyFuture.completeExceptionally(ex);
}
});
return replyFuture;
}
}
Sample Source
KafkaConfig.class
@EnableKafka
@Configuration
class KafkaConfig {
//some consumer and producer settings
//.....
//add ReplyKafkaTemplate
@Bean
fun replyingTemplate(
pf: ProducerFactory<String, String>?,
repliesContainer: ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer<String, String>?
): ReplyingKafkaTemplate<String, String, String> {
return ReplyingKafkaTemplate(pf, repliesContainer)
}
@Bean
fun repliesContainer(
containerFactory: ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<String?, String?>
): ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer<String?, String?> {
val repliesContainer = containerFactory.createContainer(replyTopic)
repliesContainer.containerProperties.setGroupId("repliesGroup")
repliesContainer.isAutoStartup = false
return repliesContainer
}
}
TestReply.class
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
class TestController(
private val testService : TestService
) {
@GetMapping("/sendEvent")
fun test(@RequestParam str : String){
val send = testService.send(str)
println("response : $send")
}
}
@Service
class TestService(
private val replyingKafkaTemplate: ReplyingKafkaTemplate<String, String, String>
){
fun send(str: String) : String {
println("in request value : $str")
val correlationId = UUID.randomUUID().toString() //응답을 추적하기 위한 고유 식별자
val record = ProducerRecord("request-topic", correlationId, str)
val future: RequestReplyFuture<String, String, String> = replyingKafkaTemplate.sendAndReceive(record) //RequestReply 호출
val response = future.get(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 타임아웃 설정
println("out response value : $response")
return response.value()
}
}
@Component
class RequestReplyKafkaListener{
@KafkaListener(topics = ["request-topic"], groupId = "reply-group")
@SendTo("reply-topic")
fun listen(message: String, @Header(KafkaHeaders.RECEIVED_KEY) key: String?): String {
println("in progress")
return "say : $message"
}
}
/*
수행 결과
2025-03-19T09:29:30.052+09:00 INFO 53177 --- [requestReplyServer] [nio-8090-exec-1] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Completed initialization in 0 ms
in request value : test
in progress
out response value : ConsumerRecord(topic = reply-topic, partition = 0, leaderEpoch = 0, offset = 28, CreateTime = 1742344170106, serialized key size = 36, serialized value size = 10, headers = RecordHeaders(headers = [RecordHeader(key = kafka_correlationId, value = [76, 34, 85, 24, 127, 127, 77, 41, -128, 121, -111, 5, 23, -93, -28, -87])], isReadOnly = false), key = eef74a7b-4190-4e50-948a-1b2d16afd792, value = say : test)
response : say : test
*/
결론
Spring 에서 제공하는 ReplyingKafkaTemplate를 활용 하여 이벤트 기반의 Request-Reply 패턴을 간단하게 구현 할 수 있었습니다.
Microservice 간 통신을 고민할때 Rest API 에만 의존 하지 말고 이벤트 기반 방식을 고민 하면 빠른 성능과 유연한 확장성을 확보 할 수 있습니다.
또한, MSK 의 Partition 기능을 활용 하면 비동기 이벤트 처리에도 순서보장을 유지 할 수 있는 구현을 할 수 있습니다.
KafkaTemplate 와 ReplyingKafkaTemplate 를 활용하면 동기 및 비동기 처리를 유연하게 구현 할 수 있으니 다양한 아키텍처에 활용 해보시기 바랍니다.